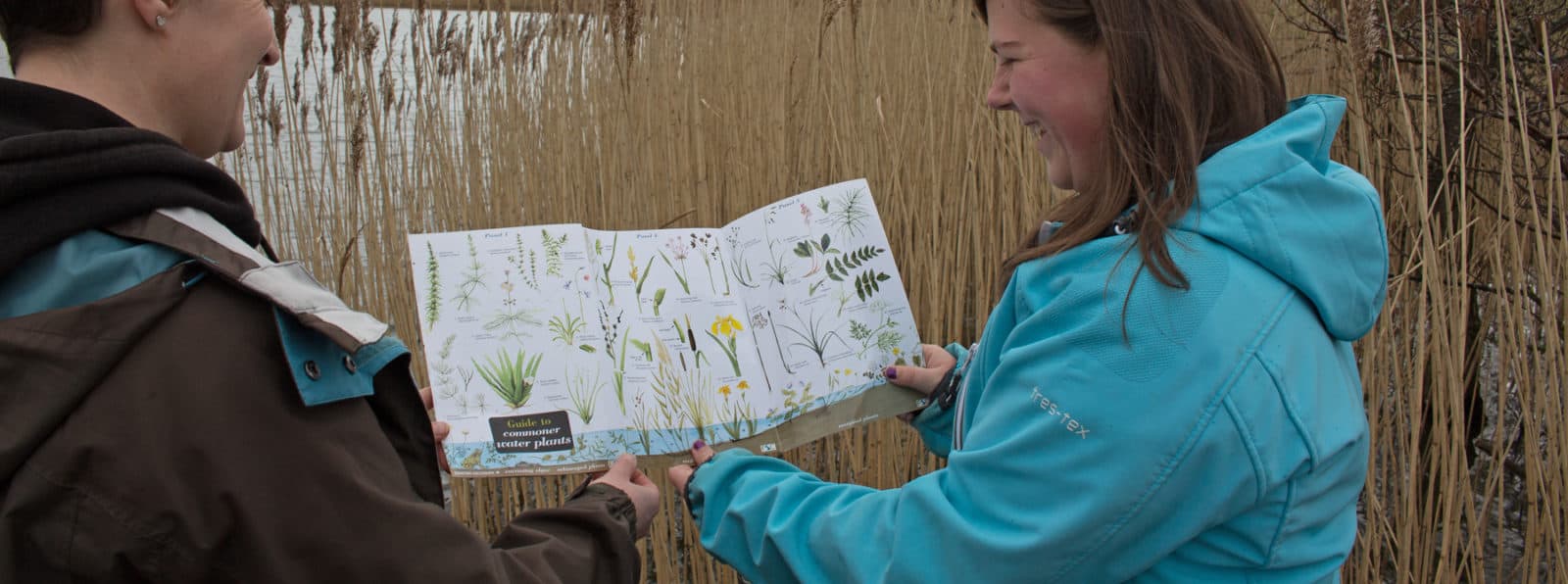
Water plants guide
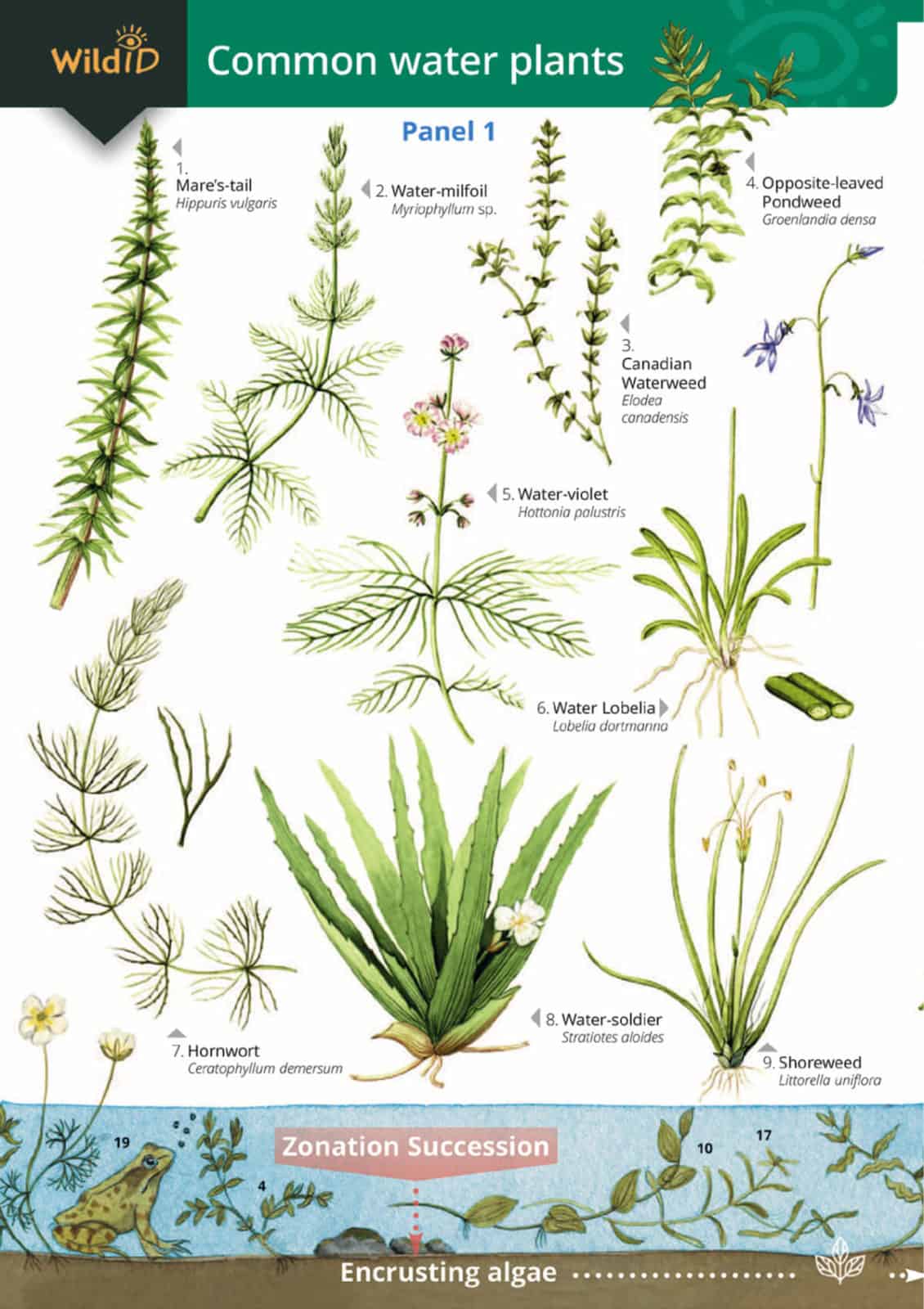
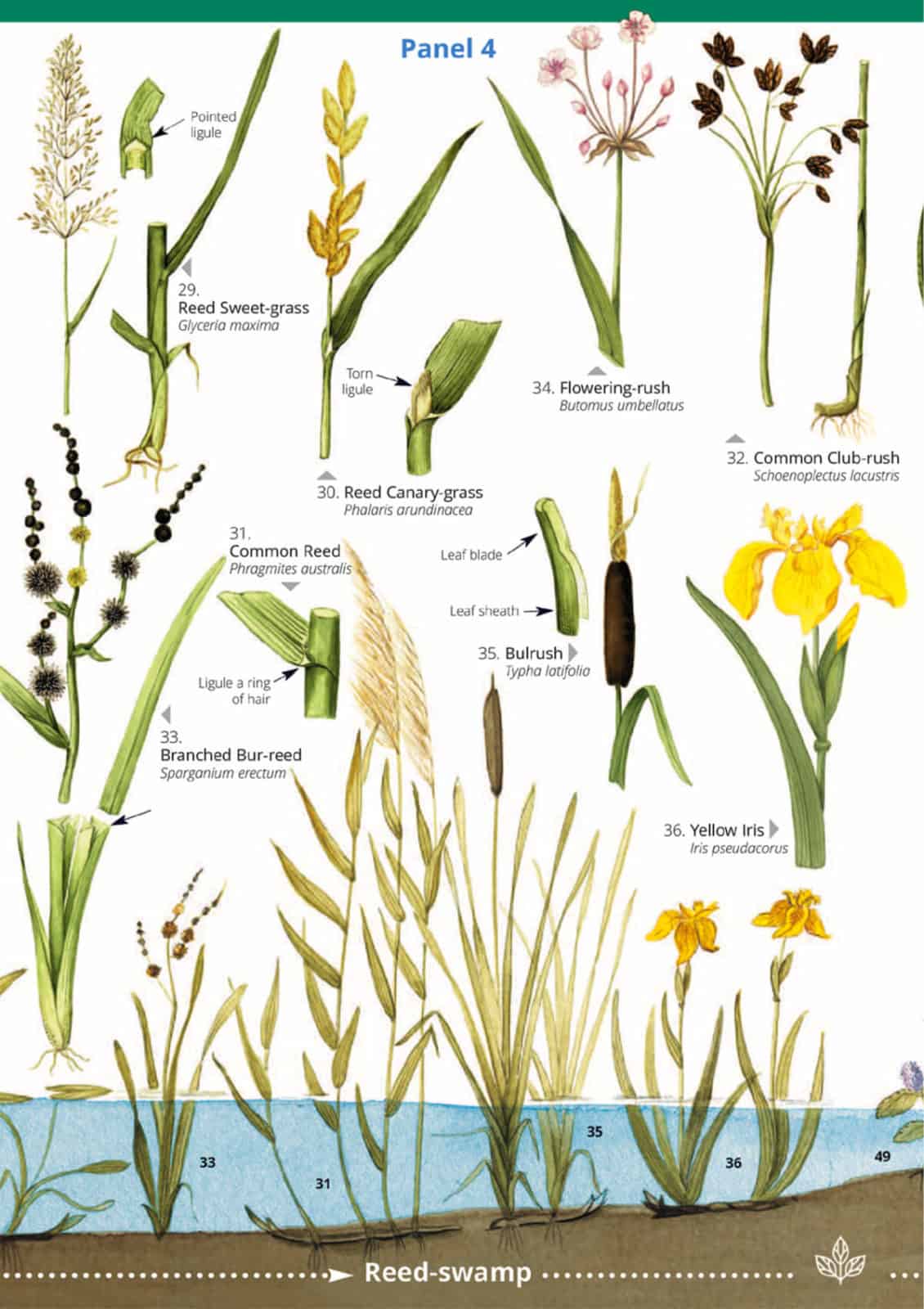
From bogbean to bulrush, from water soldier to yellow flag, the Water plants guide features 54 species of plants found at ponds, lakes, canals and slow-flowing streams and rivers.
The guide features beautiful colour paintings of each species, arranged by height, including
- Submerged plants.
- Floating plants.
- Emergents.
- Marginal plants.
Text on the reverse side looks at the role of water quality and nutrient status in the distribution of plants. Also included is concise advice on the importance of plants in garden ponds and on how to manage them. The ecological process of succession is described and illustrated in the frieze at the base of the Water plant guide. The section on ecology looks in particular at the role of water quality and nutrient status in the distribution of plants. Additionally there is advice on how to manage plants in garden ponds.
In still and slow-moving water, plants are often arranged roughly into zones. Submerged and floating plants usually colonise open water. Common water plants in ths zone include duckweed, pondweed and water crowfoot. As organic debris builds up, water depth decreases. Rooted plants with floating leaves become more abundant, forming a zone which merges into reed swamp. Then as further organic matter builds up this gives way to marginal plants. These plants tolerate both shallow water and damp soil. With time a stable commuity of land plants will develop.
The Water plants guide is ideal for students who need a quick but reliable key as part of fieldwork on freshwater succession and zonation. The guide is suitable for GCSE and A level fieldwork investigations into a hydrosere.